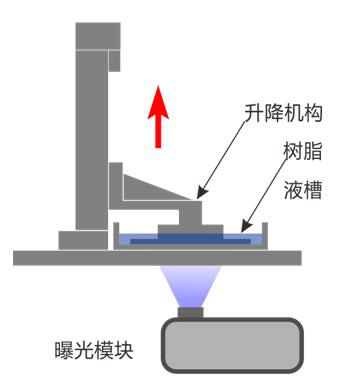
3D printing technology
3D printing technology is a kind of rapid prototyping technology, which is based on mathematical model files and uses adhesive materials such as powdered metal or plastic to construct objects through layer by layer printing. Often used in mold manufacturing, industrial design, and other fields to manufacture models, and later gradually used in the direct manufacturing of some products, there are already components printed using this technology.
This technology has applications in jewelry, footwear, industrial design, architecture, engineering and construction (AEC), automotive, aerospace, medical industry, education, geographic information systems, civil engineering, firearms, and other fields。