Spectral analysis using DMD
Spectral analysis is a powerful non-contact technology that can quickly identify the composition and related characteristics of substances by analyzing the absorption or reflection changes of different wavelengths of light in the entire spectrum.
Spectral analysis identifies a substance and determines its chemical composition and relative content based on its spectrum. According to analysis principles, spectral analysis can be divided into emission spectrum analysis and absorption spectrum analysis. Spectral analysis can support visible, infrared, or UV wavelengths.
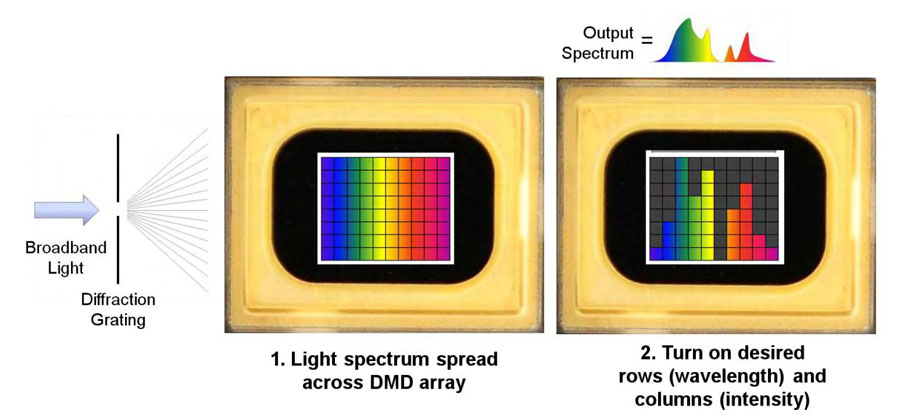
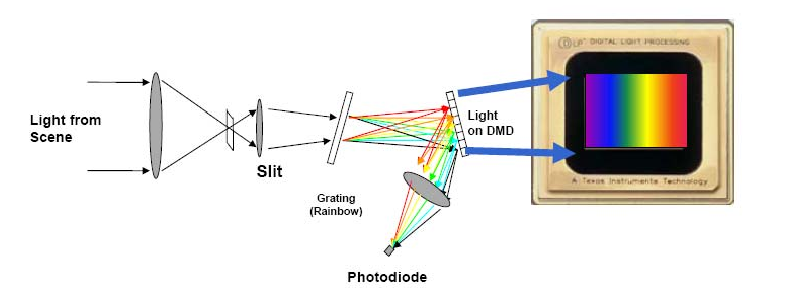
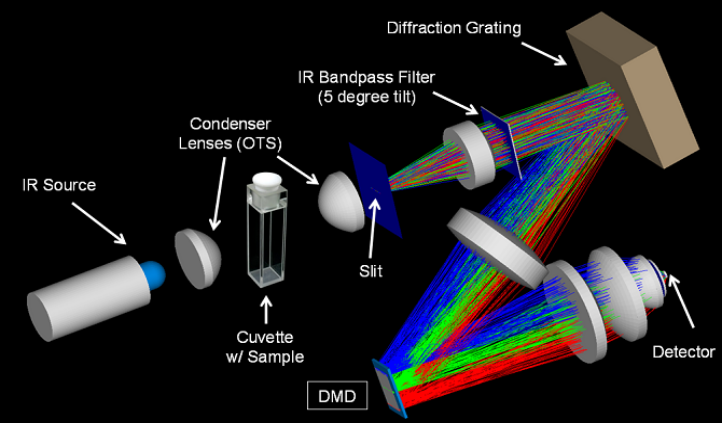
When the light source is irradiated onto the DMD array through a light splitting grating, the DMD micromirror can be used as a light splitting filter. This DMD consists of hundreds of thousands to millions of extremely small micro mirror arrays. The unique architecture of DLP DMD is easy to form a spectrometer structure, and can replace expensive array detectors with larger single detectors, while still providing a reliable optical platform.