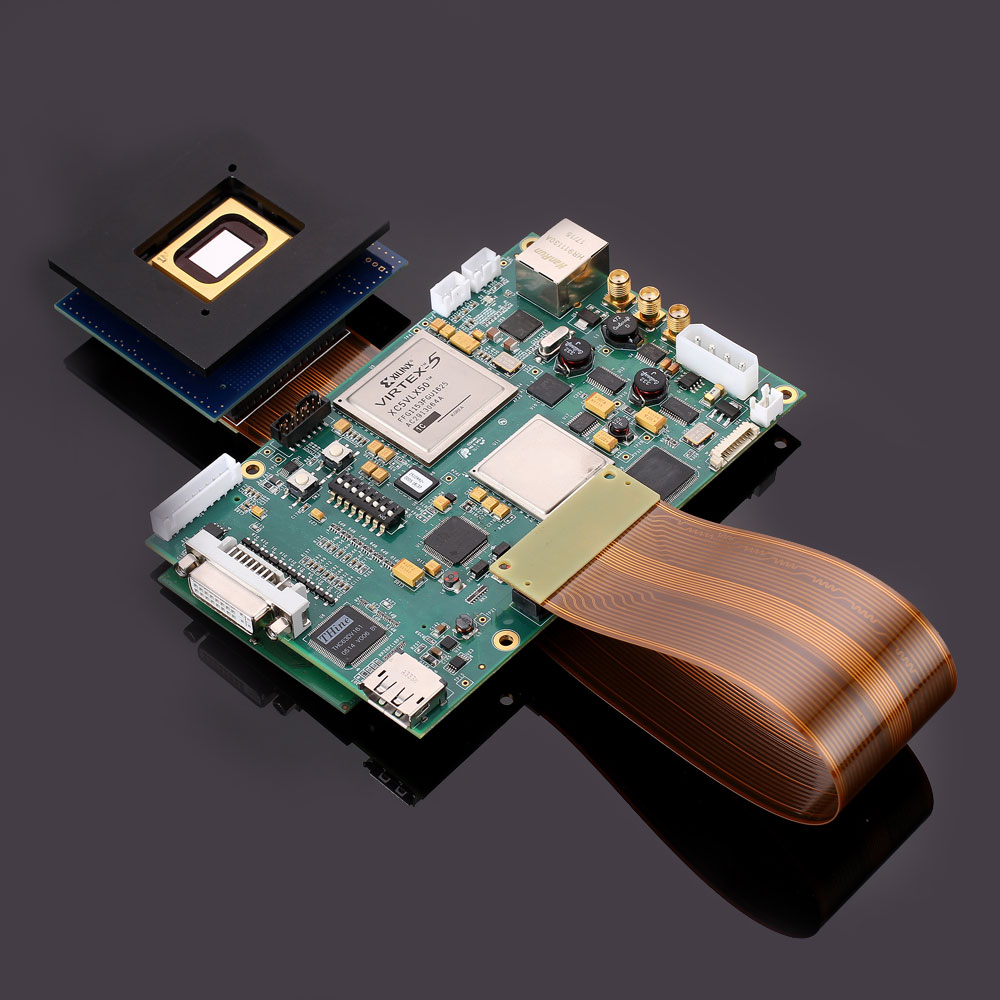
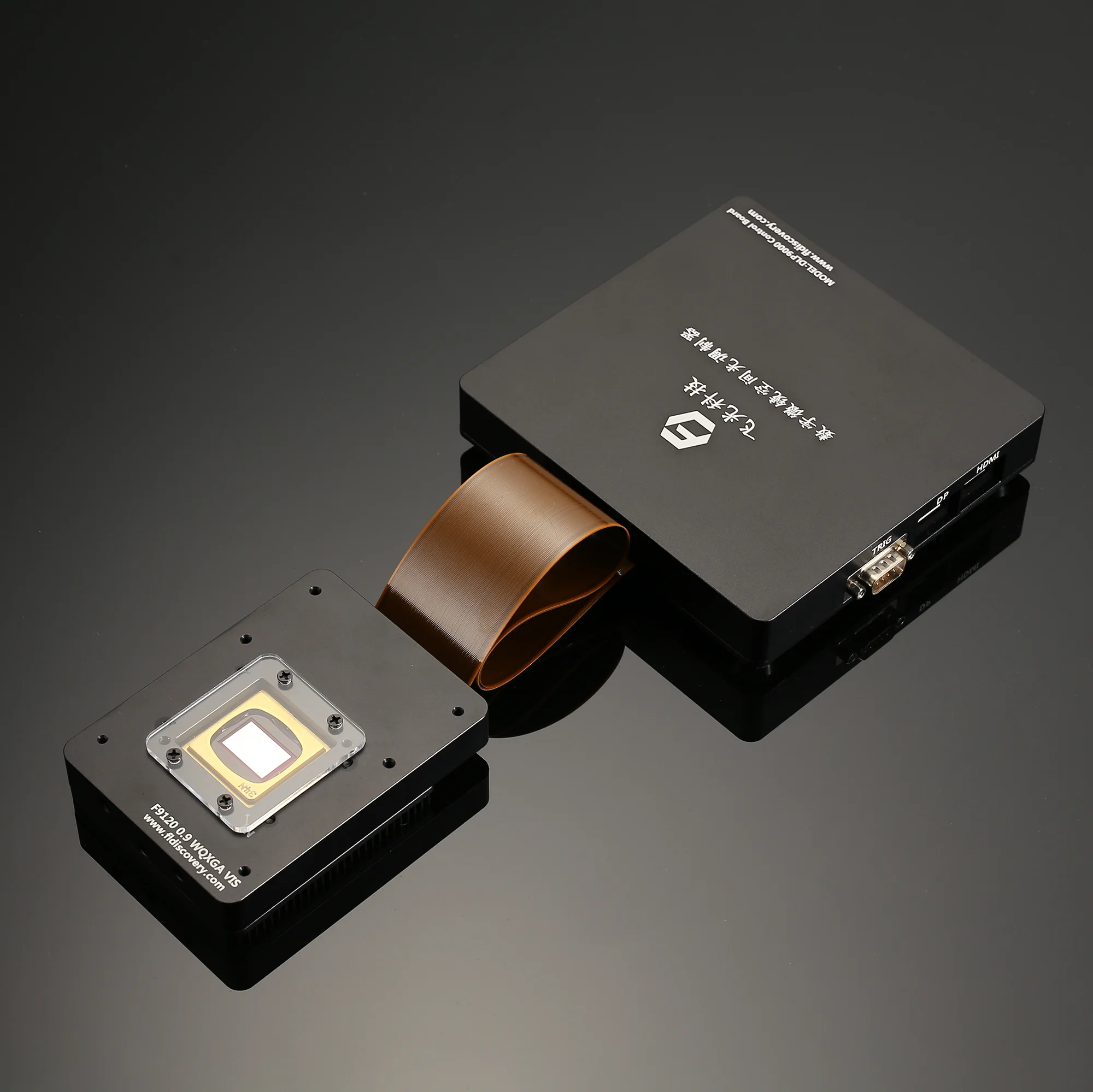
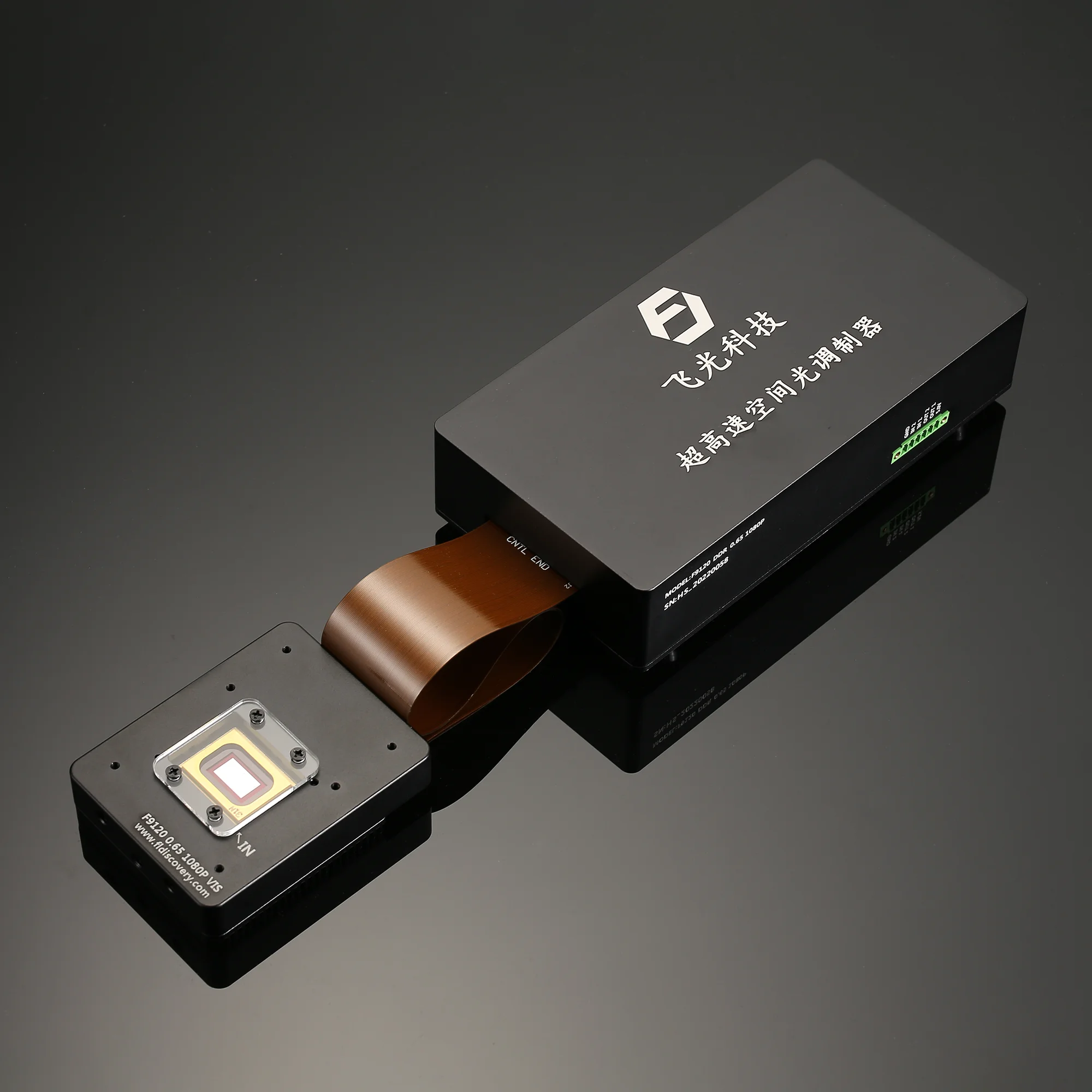
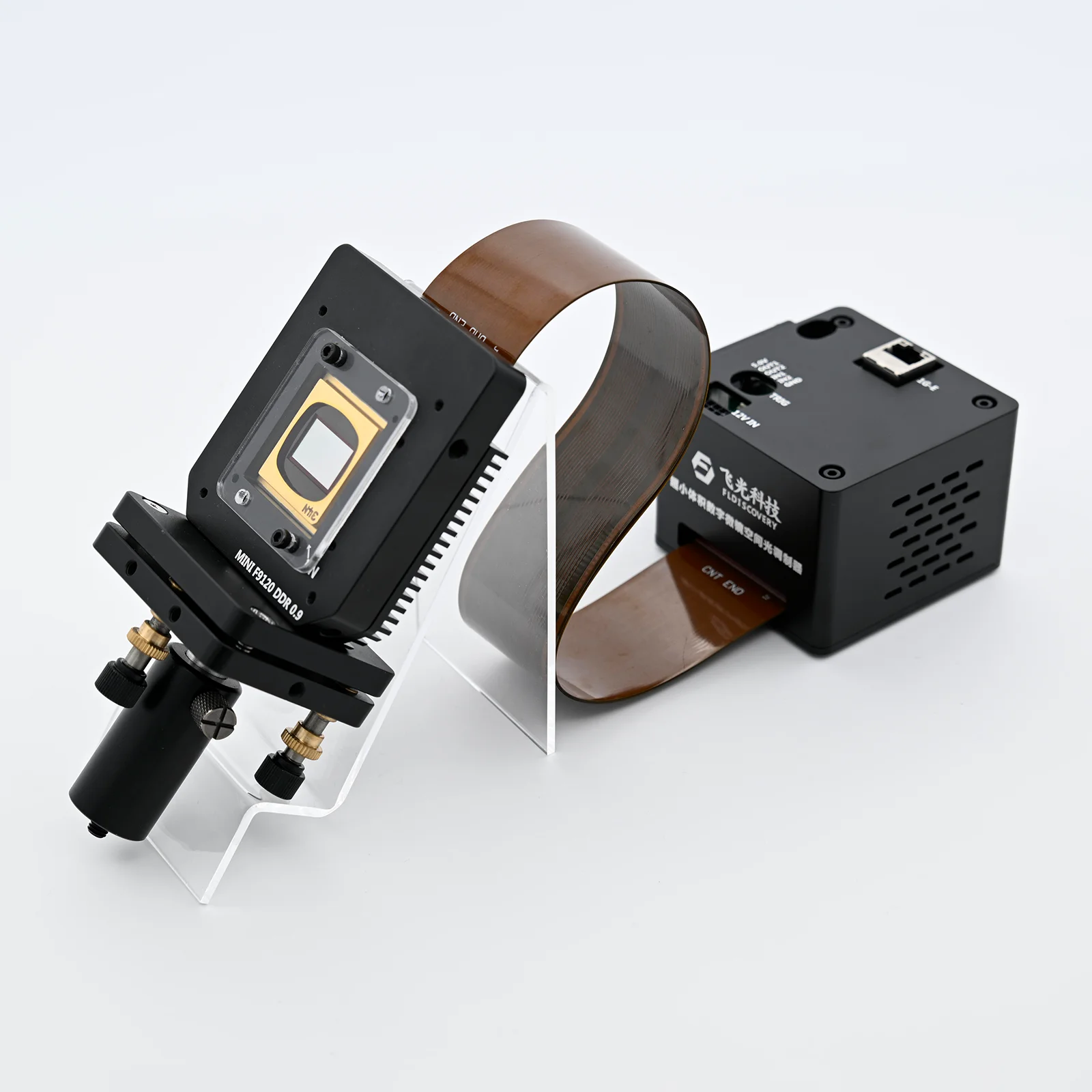
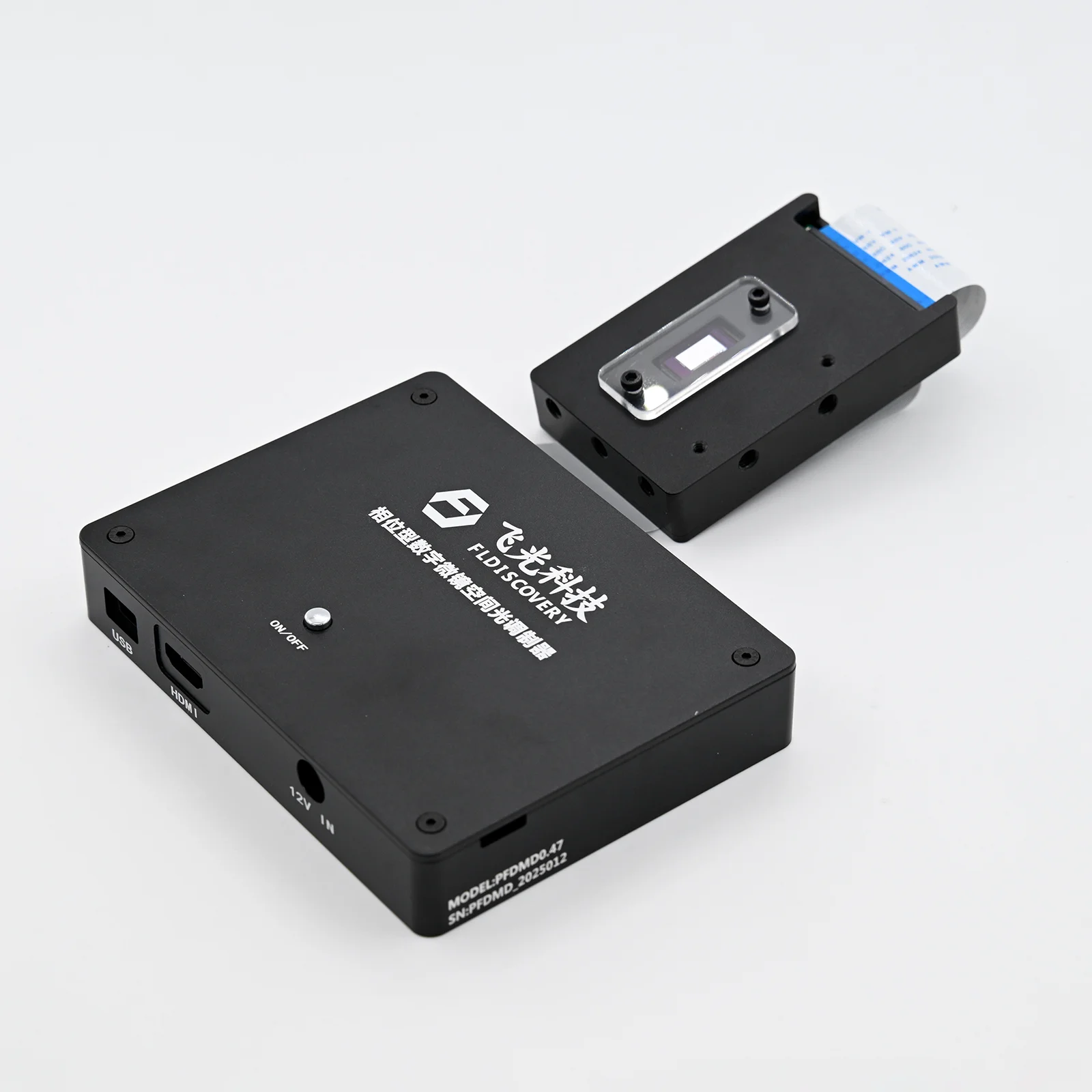
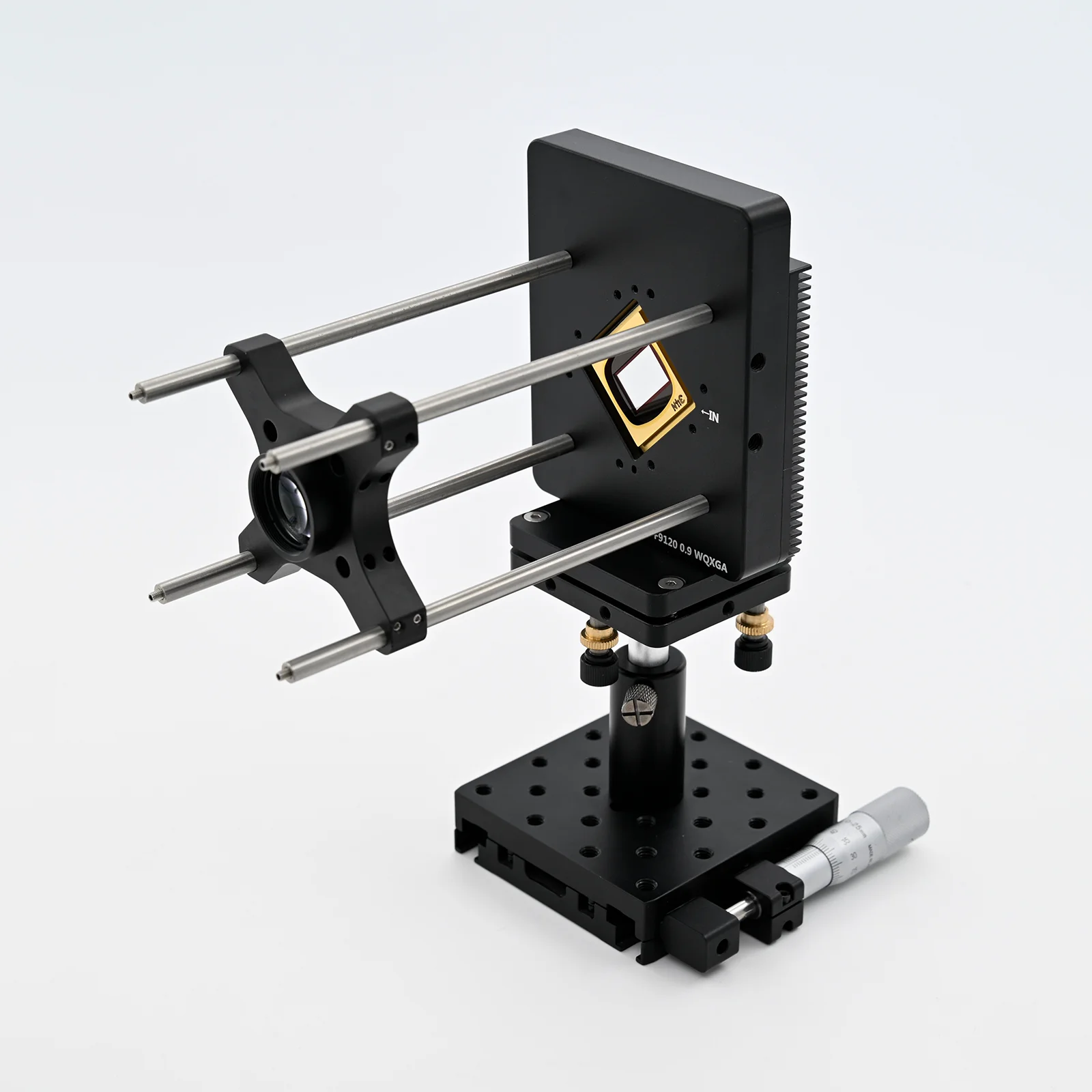
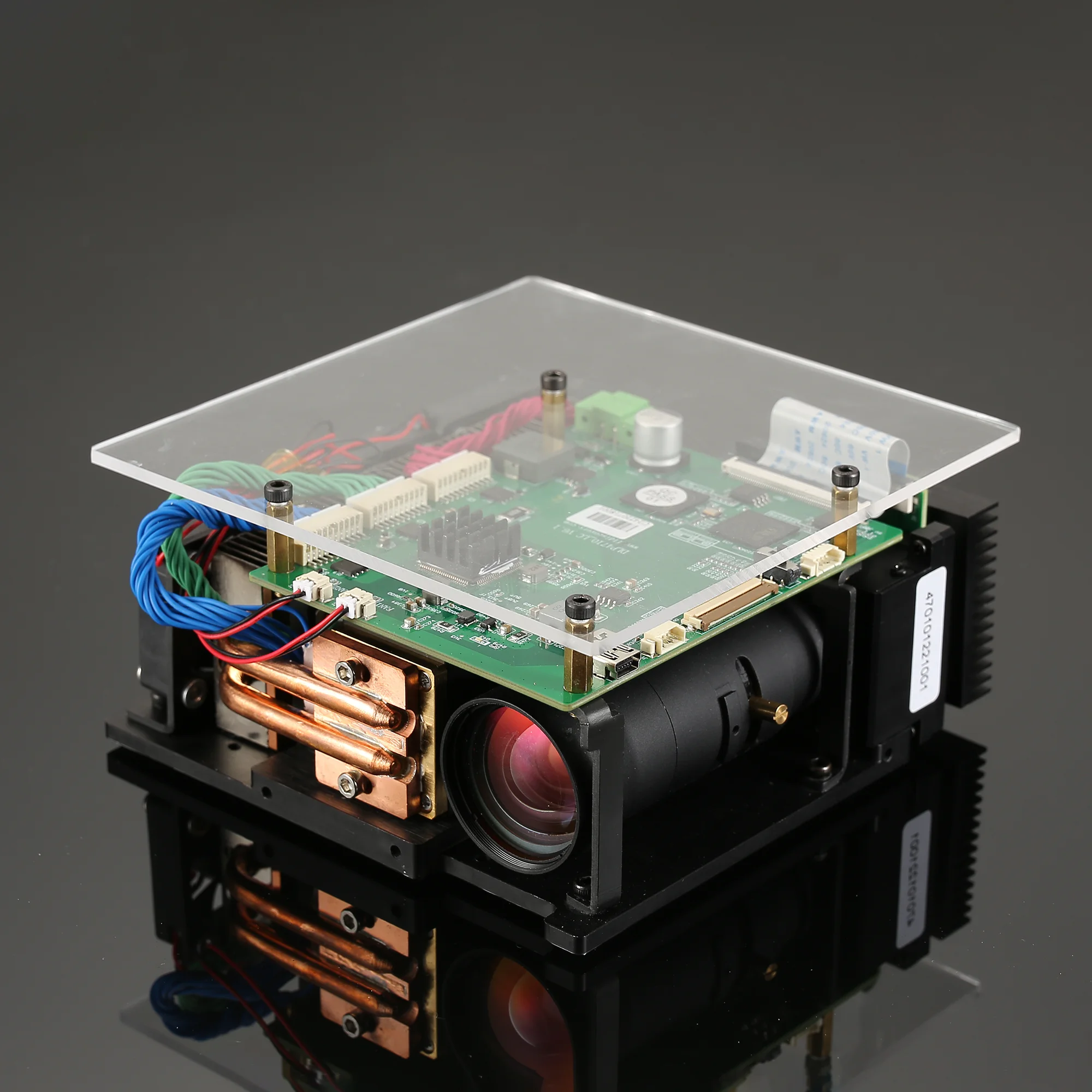
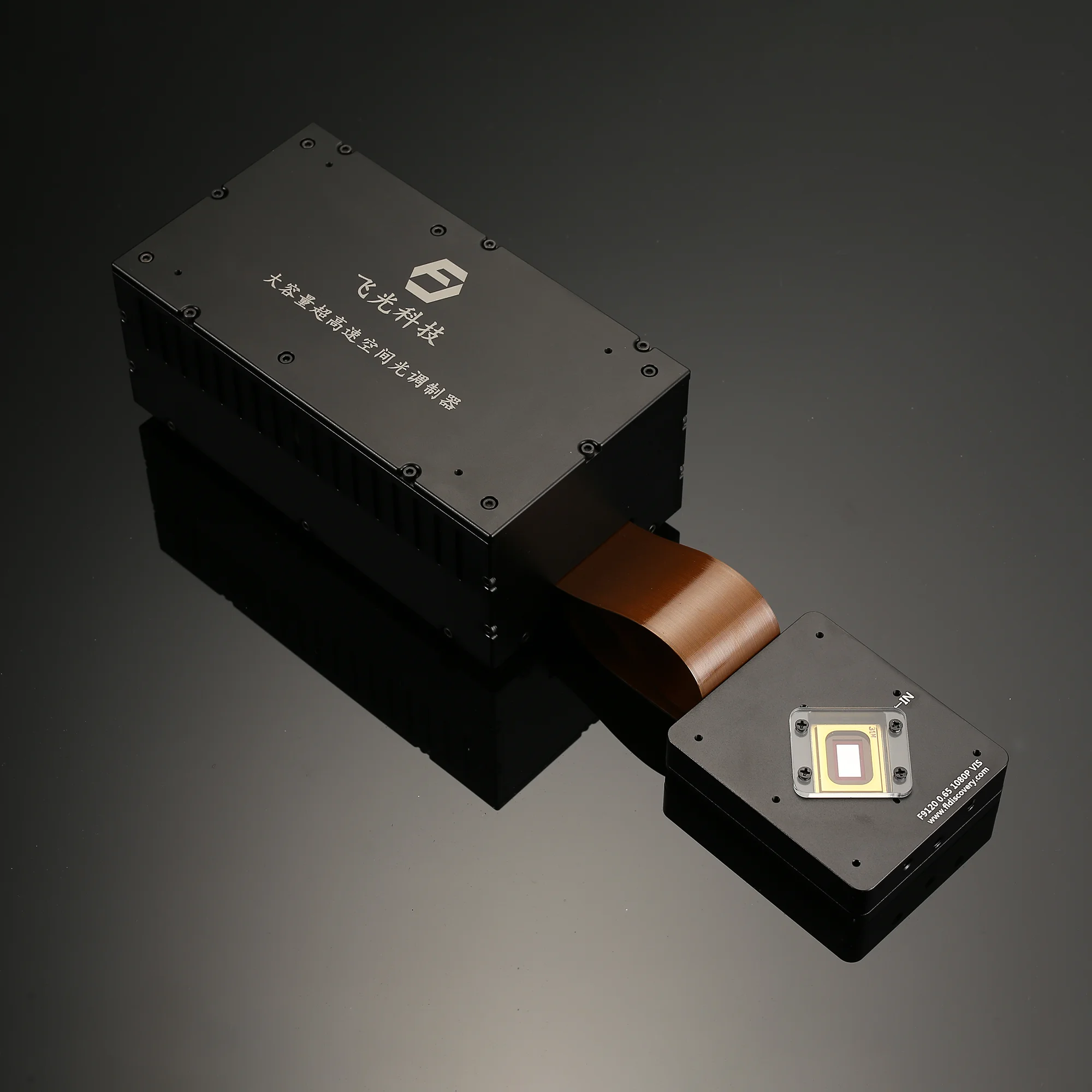
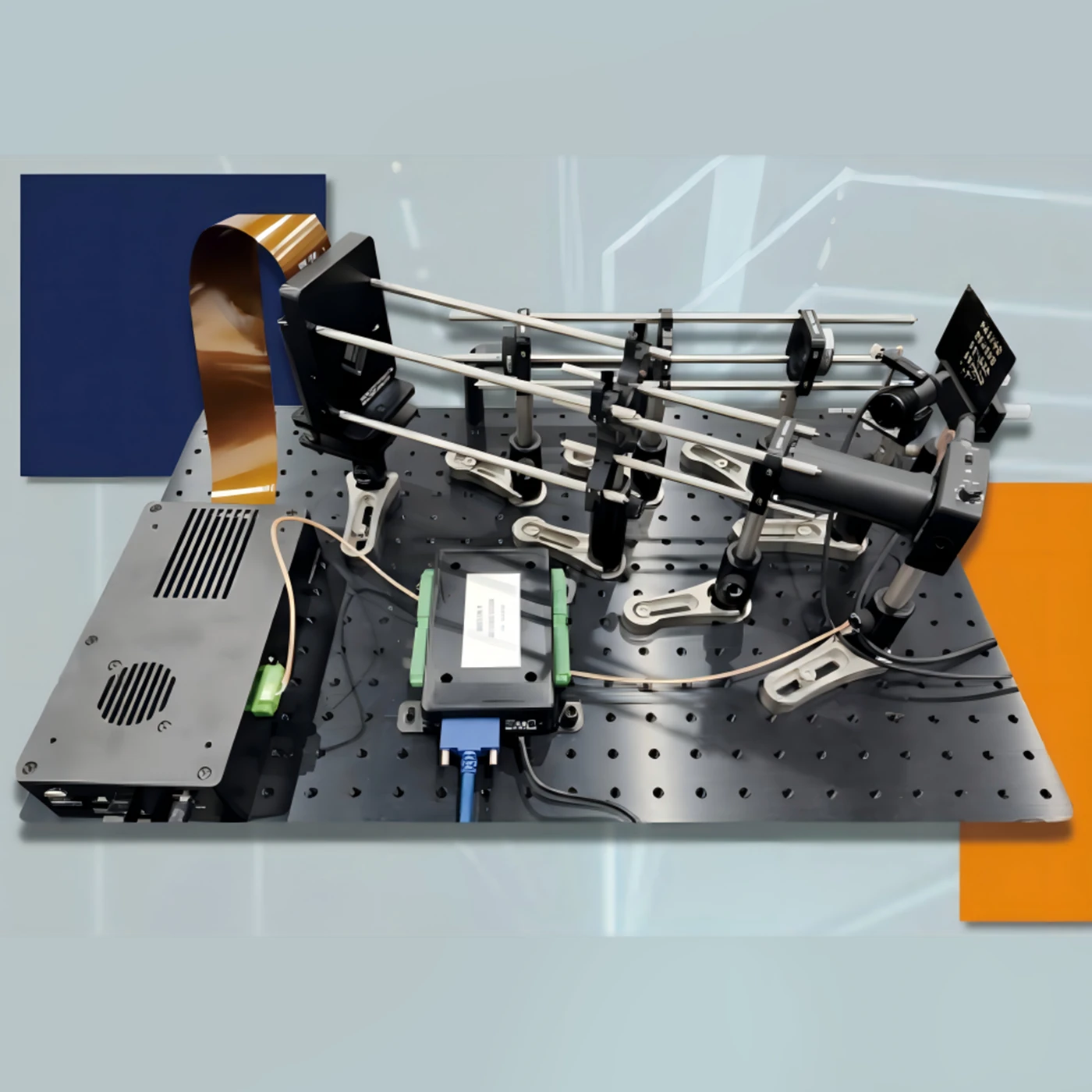
DLP Control Board
DLP control board adopts TI advanced light control chip, and adopts proven and mature technology. It is designed for industrial and scientific research fields. The biggest difference between DLP and projector is that it can support accurate internal and external synchronization, and can match with the camera. It mainly includes two parts: control and drive, which can generate programmable digital images according to user requirements, thereby meeting application requirements in the fields of machine vision, three-dimensional detection, three-dimensional scanning, computational optics, and information optics.